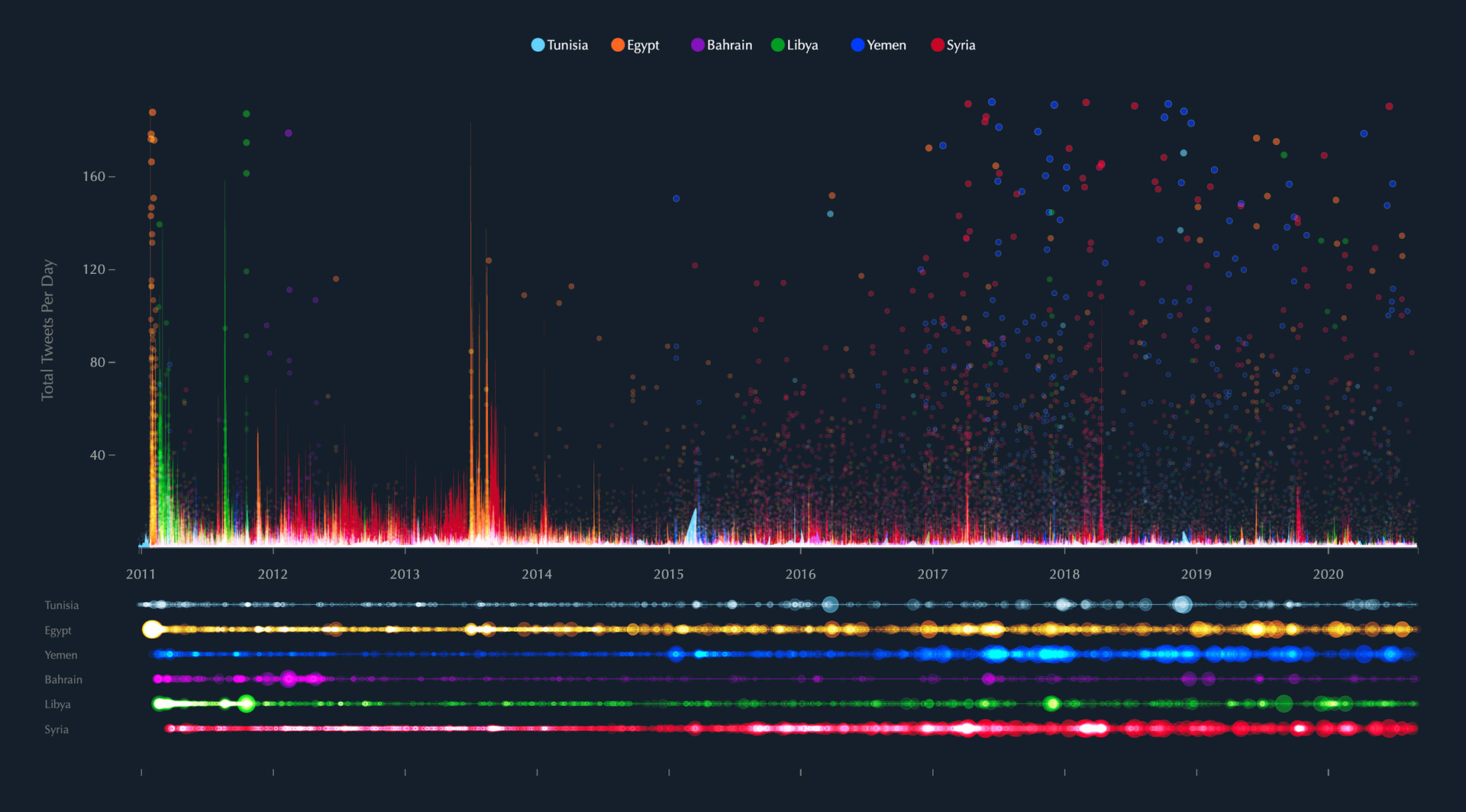
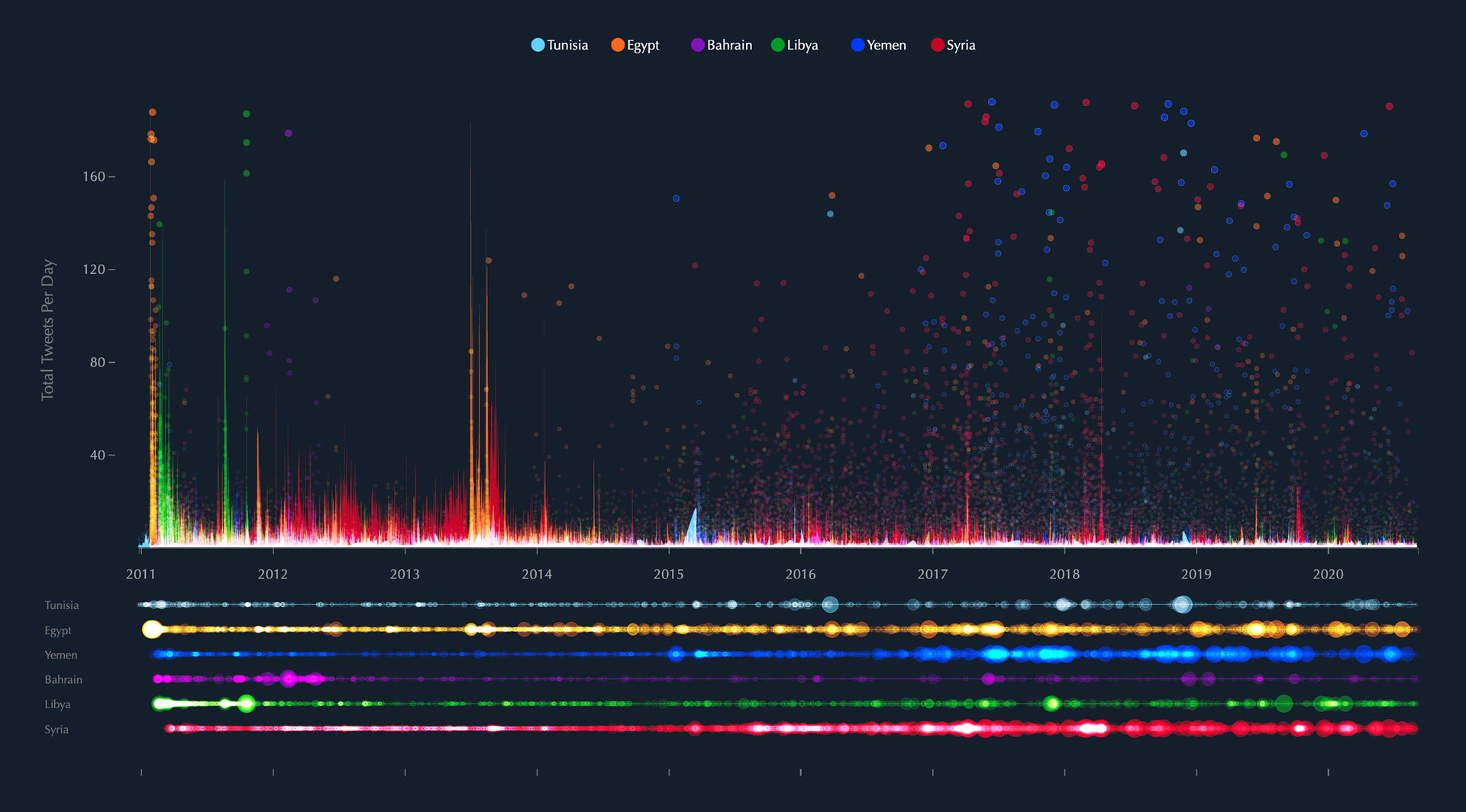
## Tunisia’s Shadowy Past: When Justice Means Death
In the heart of North Africa, a chilling echo of past injustices reverberates. Tunisia, a nation often lauded for its progressive strides, is facing a reckoning with its history. A “conspiracy trial” has reignited, casting a dark shadow over the country’s commitment to human rights. This time, the stakes are higher than ever, with the death penalty looming large.

But Tunisia’s relationship with capital punishment isn’t new. It’s a tangled web woven with threads of revolution, repression, and a struggle for a truly just society.
Global Human Rights Groups’ Response

International human rights groups, including Amnesty International, have been vocal in their criticism of Tunisia’s slide into authoritarianism. These organizations have called for immediate action to address the human rights crisis in the country, citing the arbitrary arrests, unfair trials, and crackdown on dissent.
Amnesty International, in particular, has been scathing in its criticism of President Kais Saied’s regime, labeling the detentions as “crimes against humanity” and urging the International Criminal Court to investigate the country’s leaders. The organization has also highlighted the deteriorating human rights situation in Tunisia, citing the mass detentions, one-man rule, and lack of progress on improving the economy.
Other human rights groups have echoed Amnesty International’s concerns, calling for the international community to pressure Tunisia to respect human rights and the rule of law. These organizations have also urged Tunisia to release all political detainees and to respect the rights of freedom of expression and assembly.
The Geopolitical Implications
Regional Instability and Authoritarianism
Tunisia’s slide into authoritarianism has significant implications for regional stability. The country’s descent into authoritarianism is likely to embolden other authoritarian regimes in the region, leading to a deterioration in human rights and the rule of law across the Middle East and North Africa.
The spread of authoritarianism in the region is likely to have far-reaching consequences, including the suppression of dissent, the erosion of democratic institutions, and the entrenchment of human rights abuses. This, in turn, is likely to lead to increased instability, conflict, and humanitarian crises in the region.
International Pressure and Diplomatic Fallout
The international community has a critical role to play in addressing the human rights crisis in Tunisia. International pressure, including diplomatic condemnation and economic sanctions, can be an effective way to pressure the Tunisian government to respect human rights and the rule of law.
However, the effectiveness of international pressure depends on the coordinated efforts of the international community. The lack of a unified response to the crisis in Tunisia has limited the impact of international pressure, allowing the regime to continue its crackdown on dissent with impunity.

Tunisia’s Transition to Democracy
The current situation in Tunisia has significant implications for the country’s transition to democracy. The erosion of democratic institutions, the suppression of dissent, and the entrenchment of human rights abuses are all major setbacks to Tunisia’s democratic transition.
The prospects for a return to democratic governance in Tunisia are uncertain, and the country’s future hangs in the balance. The international community must continue to pressure the Tunisian government to respect human rights and the rule of law, and to support civil society and democratic forces in the country.

The Human Cost and Practical Aspects
Human Rights Activists’ Struggle
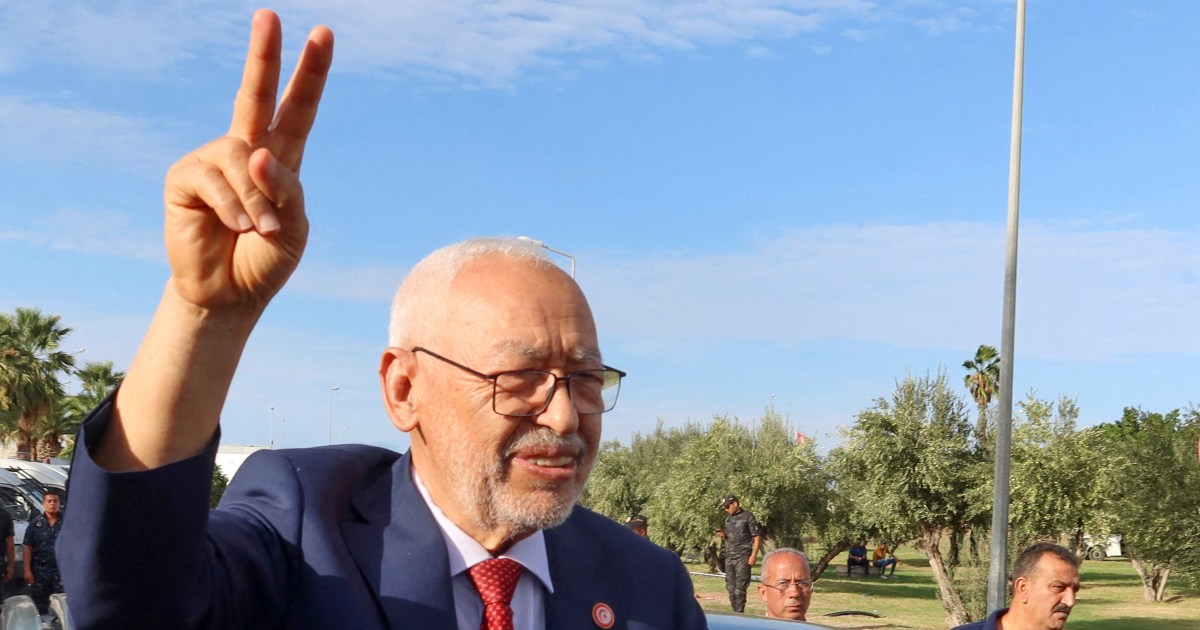
Human rights activists, including those from the Ghannouchi family, have been at the forefront of the struggle against President Saied’s regime. These activists have faced arbitrary arrests, unfair trials, and harassment, but they continue to speak out against the regime’s human rights abuses.
The personal stories of these activists are a testament to their bravery and determination. Despite the risks, they continue to challenge the regime, calling for respect for human rights and the rule of law.

Arbitrary Arrests and Unfair Trials
The arbitrary arrests and unfair trials in Tunisia have had a devastating impact on individuals, families, and communities. The detainees, including opposition politicians, activists, and scholars, have been subjected to inhumane conditions, torture, and forced confessions.
The effects of these arrests and trials are far-reaching, causing immense suffering to the detainees and their families. The lack of due process and the disregard for human rights have also undermined trust in the justice system and the rule of law.
Economic Consequences and Protests
The economic consequences of President Saied’s policies have been severe, with the country’s economy deteriorating rapidly. The lack of progress on improving the economy has led to widespread protests and discontent, with many Tunisians calling for the president’s resignation.
The protests, which have been met with violence and repression, are a testament to the depth of discontent in Tunisia. The economic crisis, coupled with the human rights abuses, has created a toxic environment, which is likely to lead to further instability and conflict.
Conclusion
The recent restart of the “conspiracy trial” in Tunisia, with its potential for death sentences, has thrown a harsh spotlight on the country’s fraught relationship with capital punishment. As Al Jazeera’s report details, Tunisia’s history with the death penalty is a complex one, marked by periods of abolition and reinstatement, reflecting the evolving political and social landscape. While the current government maintains a stance against arbitrary executions, concerns remain about the fairness and transparency of these trials, especially given the politicized nature of the charges against the accused.
This case underscores the ongoing struggle for justice and human rights in Tunisia, and highlights the delicate balance between security concerns and individual liberties. The international community’s scrutiny will undoubtedly continue to play a crucial role in shaping the outcome of this trial and influencing Tunisia’s future stance on the death penalty. Will this be a turning point, pushing Tunisia towards a permanent abolition of capital punishment, or will it solidify the country’s place among those who continue to use this irreversible punishment? The world is watching, and the answer will have profound implications not only for Tunisia, but for the global human rights landscape.
Ultimately, the fate of these individuals hangs in the balance, a stark reminder that the pursuit of justice must always be tempered by the fundamental respect for human life.






